In
this assignment you will be adding some more common commands
to your collection. All of these commands are ones that you
will use on a regular basis.
Command |
Keystroke |
Icon |
Location |
Result |
Move |
Move
/ M |

|
Home > Modify > Move |
Moves
an object or objects |
Copy |
Copy
/ CP |

|
Home > Modify > Copy |
Copies object(s) once or multiple times |
Stretch |
Stretch
/ S |

|
Home > Modify > Stretch |
Stretches an object after you have selected a portion of it |
Mirror |
Mirror
/ MI |
|
Home > Modify > Mirror |
Creates
a mirror image of an object or selection set |
This
is a short assignment to show you how these commands are used.
You will recreate the drawing called Assignment #4.
Click HERE to
see the file in GIF format.
Click HERE to download the
DWG file.
Start up AutoCAD and set up your drawing as you have in the previous assignments.
Turn on your Endpoint Osnap. 
This time draw the border first. Draw a 10" wide by 7" high
rectangular border using any method. The bottom left corner
must be at 0,0
Draw a 2" wide by 3" high rectangle using the
RECTANGLE command.
The bottom left corner must be at 0,0
Notice that the small rectangle and the border are overlapping
each other at the bottom left of your drawing. What
you want to do is move the small rectangle over 1" and up 1" so
that it is away from the border.
To do this, start
the MOVE command
by typing in either M or MOVE <ENTER>.
Select all the lines of the rectangle using one of
the selection methods described earlier. Press <ENTER>.
Now AutoCAD asks for a "base
point or displacement". What it is needing
is a reference point. Click on the bottom left corner
of the rectangle. AutoCAD now asks for a 'second
point of displacement'. What it needs to
know now is how far you want to move it. This is a
great time to use relative coordinates. In this case,
you want to move it 1" over and 1" up. So type @1,1 <ENTER> to achieve this. The rectangle will automatically move
to its new location.
Now
you want to copy this rectangle 3" over
to the right. The copy command is very similar to the
move command. (The only difference is that the copy command
leaves an original behind.)
Start the COPY command.
You will be asked to select objects. Select the rectangle
you just moved. AutoCAD now needs the "base
point or displacement" just like in the move command.
Once again, select the bottom left corner of the rectangle.
Once you've done this, you need to tell AutoCAD what
the second point of displacement is. Since you want to
move the rectangle over 3" to the right, type in @3,0 <ENTER> The rectangle has now been copied 3" over.
BREAK TIME : Copy and move are 2 commands that you use a lot with AutoCAD. Both commands work the same way in terms of the steps you take. Learn to use these commands well - you'll need them. Honestly. Being quick with these commands makes you a much better drafter. |
But
the rectangle is not as tall as the one in the sample
drawing, the sample drawing's rectangle is 1" taller. To
modify this, you'll use the stretch command.
Start the STRETCH command
by typing S <ENTER>.
AutoCAD now makes you select objects by using a crossing
window or crossing polygon. You're going to use a crossing
selection. Remember from the Lesson 1-5 that you make a crossing
selection by creating it from the right to left. Left-click
just a bit above and to the right of the top right hand
corner of the new rectangle (P1). Move your crosshairs down
and to the left until your (dotted) crossing window covers
the top half of the rectangle completely and then left
click again (P2). You'll see that the objects are highlighted
now. Press <ENTER> to accept this. Next you're
asked for that now familiar base point. Pick on the top
left corner of the rectangle. Now give AutoCAD the second
point of displacement. In this case, you want to stretch
the rectangle 1" up, so type @0,1 <ENTER> to do this. The rectangle is now 1" taller.
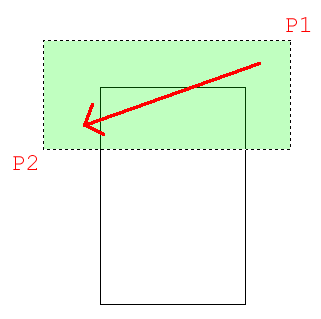
The goal when selecting objects to stretch is to draw the window over the vertices or points that you want to stretch. If you miss a corner, you will change the shape of the rectangle. So always be aware of which points need to be stretched. In this example, it was pretty obvious, in more complex drawings - it won't be.
Next you want to draw the polygon on the right side. To
do this, you will draw the three lines on the left side first
and then mirror those lines over to the right side. Draw
the 3 lines any way you like (hint: use absolute coordinates.).
Once they are drawn, begin the MIRROR command.
Select the three lines (press <ENTER>) Now you are asked
for the first point of the mirror line. With your endpoint
Osnap turned on, pick the end of the line at 8,2.
Now you are asked for the second point. Select the point
on the line at 8,5.
Once you've done this, AutoCAD wants to know if you want
to delete the old objects. In this case you don't, so accept
the default by pressing <ENTER>. The mirror
line will be half-way between the object the you are mirroring
and where you want it to be. Figuring out where the mirror line is the toughest part of this command.

The
assignment is now complete. Review what you have done and practice
on these commands. Save and print your assignment. Copy and Move are very common commands. For example, you might create a ceiling light, then have to move it into place, and then copy it to other rooms. Fortunately, these commands work very similar, and once you master one, you have mastered both.
Extra Practice: Copy this drawing using the commands you have learned in lessons up to this point - extra_007.gif
Extra Practice: This exercise uses an option of the CIRCLE command called "Tangent Tangent Radius" or TTR. To use it, pick the two tangents of the circle first, then enter the radius. The rest of it uses previous commands. extra_008.gif This one is tricky, so try it a few times before checking the video.
 RETURN
TO THE TOP OF THE LESSON | RETURN TO THE TABLE OF CONTENTS RETURN
TO THE TOP OF THE LESSON | RETURN TO THE TABLE OF CONTENTS
CONTINUE TO THE NEXT LESSON - 1-7 >
|